GORILLA AND CHIMPANZEE TREKKING PRICES
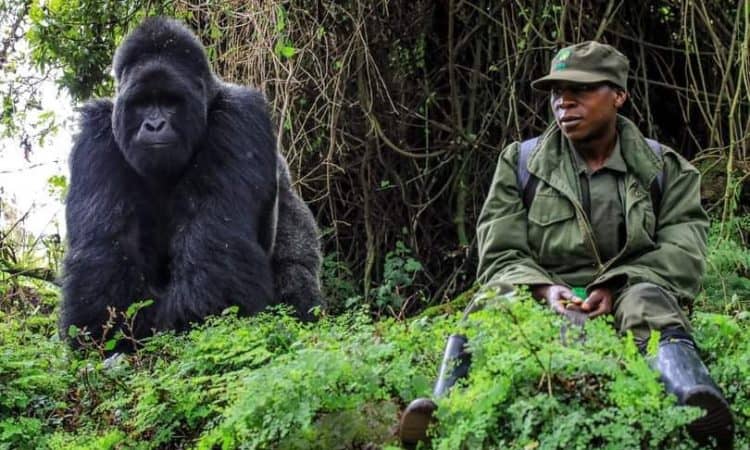

Effective from April 1, 2024, the Uganda Wildlife Authority (UWA) has implemented new tariffs for gorilla and chimpanzee trekking permits, marking a significant shift for travelers seeking the unique experience of observing primates in their natural habitats. These adjustments reflect Uganda’s ongoing commitment to conservation, tourism, and the protection of its wildlife. With the changes already in effect, both prospective travelers and industry stakeholders must adapt to the new costs, which will ensure long-term sustainability and contribute to critical conservation efforts.
New Gorilla Trekking Tariffs in Uganda
As of April 2024, the cost for gorilla trekking permits has increased from $700 to $800 per person, per trek. This tariff applies to both Bwindi Impenetrable National Park and Mgahinga Gorilla National Park, which are globally renowned for their populations of critically endangered mountain gorillas. Uganda, home to over half of the world’s remaining mountain gorillas, offers one of the most thrilling wildlife experiences for eco-tourists.
Gorilla trekking in Uganda remains a highly sought-after activity, and the increase in permit costs is expected to maintain the delicate balance between human interaction and conservation efforts. Each trekking permit allows participants to spend one hour observing a habituated gorilla group under the supervision of expert guides and rangers. The raised price reflects the rising costs associated with managing and protecting the gorillas’ habitat, as well as ensuring the safety and health of the animals.
Changes to Chimpanzee Trekking and Habituation Permits
In addition to the changes in gorilla trekking permits, chimpanzee trekking in Kibale Forest National Park has also seen an increase in permit fees. The price for a standard chimpanzee trekking permit has risen from $200 to $250 per person. Kibale Forest, often referred to as the “primate capital of the world,” is home to numerous chimpanzee families, making it a hotspot for primate tracking.
For those seeking a deeper, more immersive experience, the chimpanzee habituation permits now cost $300, up from $250. The habituation experience allows participants to spend extended time—up to four hours—with chimpanzees as they become accustomed to human presence. This is a rare opportunity to witness the chimps’ behavior over an extended period, providing a richer understanding of their social dynamics and daily routines.
In the Kyambura Gorge within Queen Elizabeth National Park, the cost of chimpanzee trekking permits has increased significantly, from $50 to $100. Known as the “Valley of Apes,” Kyambura Gorge offers a scenic but challenging trekking experience and is one of the best locations in Uganda to track chimps in the wild
Impact of the Tariff Changes
The new tariffs for gorilla and chimpanzee permits have important implications for Uganda’s conservation initiatives, local communities, and the overall tourism industry. By raising the prices, Uganda is enhancing its ability to protect endangered species and their habitats. The revenue generated from the permits is directly reinvested into wildlife protection, habitat restoration, and anti-poaching measures.
The increase in permit prices also reflects the growing demand for primate trekking experiences, especially among international travelers. With Uganda continuing to be a premier destination for eco-tourism, the new tariffs are likely to maintain the exclusivity of gorilla and chimpanzee trekking, ensuring that these activities are conducted responsibly with minimal impact on the environment and wildlife.
For local communities living near national parks, the increased permit prices are good news. A portion of the revenue generated is channeled into community development projects, which support education, healthcare, and infrastructure. These initiatives help improve the quality of life for residents, creating a positive relationship between conservation efforts and local livelihoods
The Value of Sustainable Tourism
Sustainable tourism lies at the heart of Uganda’s wildlife management strategy. Mountain gorillas, in particular, are extremely sensitive to human interaction, and the restrictions on the number of trekking permits issued daily help mitigate any potential stress on the animals. The new tariffs are designed to ensure that gorilla and chimpanzee trekking remain sustainable practices that contribute to conservation without overwhelming the natural environment.
Uganda issues only eight permits per habituated gorilla group per day, meaning that just over 200 permits are available daily across Bwindi Impenetrable National Park and Mgahinga Gorilla National Park. The limited number of permits, combined with the new price increase, helps to control the number of tourists and ensures that the gorilla populations are not unduly affected by human presence
Preparing for Your Trekking Adventure
With these tariff changes already in place, travelers planning their trekking safaris in Uganda should be mindful of the new costs. Booking permits well in advance is crucial, especially during peak seasons, when availability is limited. Most tour operators offer packages that include the cost of trekking permits, along with accommodation, transport, and meals. However, travelers should be aware of the additional costs associated with their safari, such as park entry fees and accommodation, which are not included in the trekking permit.
Travelers looking for a more exclusive experience may opt for the habituation permits, particularly for chimpanzees. While more expensive, these permits provide a rare opportunity to spend an extended time observing these primates in their natural environment, making the experience more intimate and rewarding.